Automotive & Industrial Lubricants and Greases Manufacturer
We believe in creating a future where innovation meets responsibility. We are dedicated to providing forward-thinking solutions
that empower businesses and communities to thrive sustainably. With a blend of expertise and a commitment to excellence,
we partner with you to build impactful, Eco-conscious results that benefit the world today and tomorrow.
Automotive Oils
We specialize in engine oils for four-wheeler, two-wheeler, diesel engines, and pumps. We also manufacture Automotive and Industrial greases and Coolants for vehicles. →


Greases
We specialize in manufacturing a wide range of high-quality greases tailored for both Automotive and Industrial applications
.→
Industrial Oils
We offer a comprehensive range of products designed to meet the needs of various industries, from general purpose lubricating oils to specialized fluids.
→


Auto Care Products
We introduced a variety of polishes, cleaners, shampoos, fresheners, and paint products that will add beauty to your car, Jeep, scooter and bike. →
Who are we?
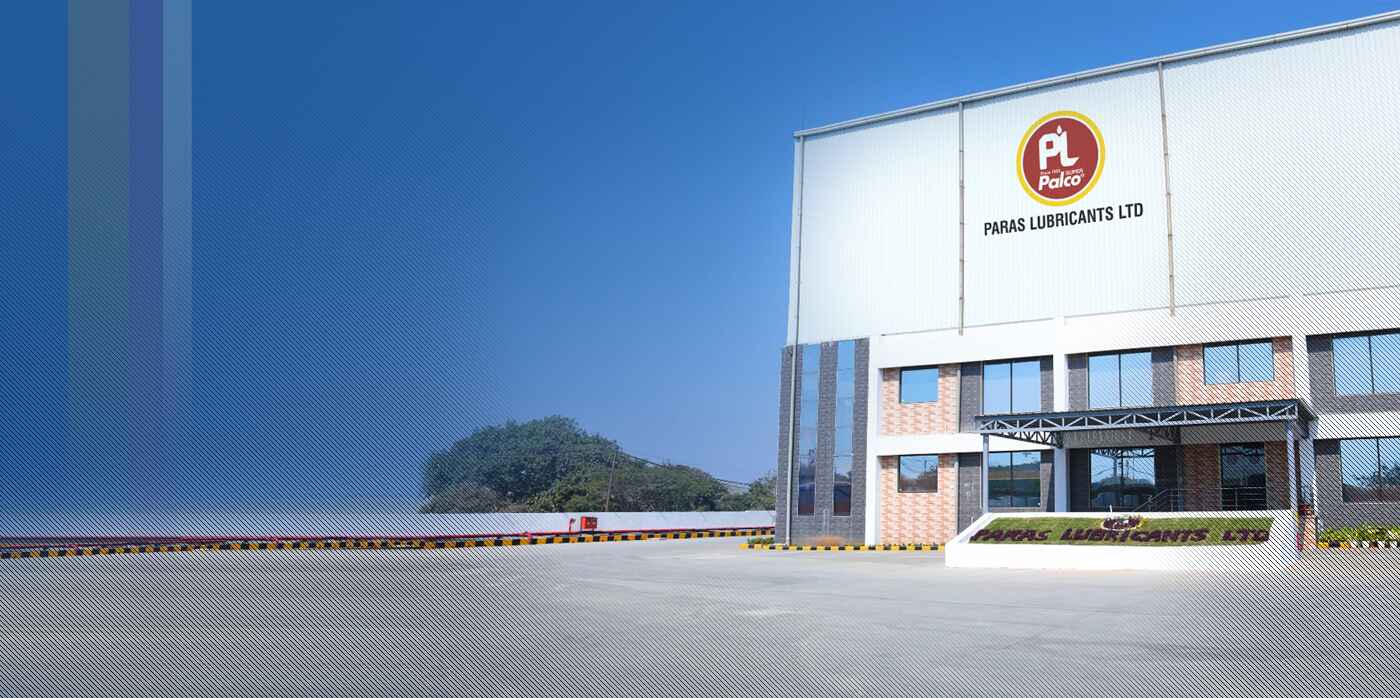
Paras Lubricants Limited was incorporated in 1985 as Private Limited Company and subsequently converted into Public Limited Company in 1995. The Company’s Head Office is in Delhi and Western Office is in Mumbai. The overall marketing, administrative matters and the day-to-day activities of the Company are looked after from these two offices. The Company’s products are marketed under the trade name “PALCO” Lubricants are manufactured at two plants located at Khopoli, (Dist. Raigarh, Maharashtra) and Daman (U.T.).
To provide quality products at a price that reflects true value along
with unparalleled support services by highly trained and
well-motivated work force meeting customer
expectations and requirements.
To be the foremost Indian Lubricant Manufacturing Company
most admired for its quality products, reliable performance and
best services with a perspective of global excellence.
Our Mission and Vision statement consists of the following values.
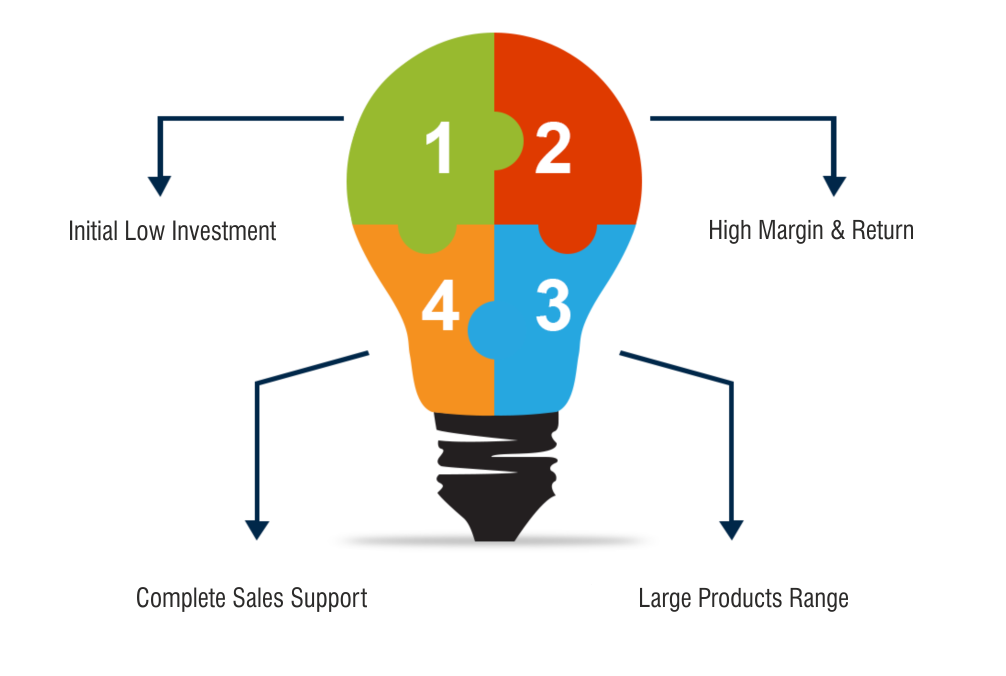
New Business Opportunity
let’s work together
Growing your dealer/distributor business means having products and selling programs that satisfy your customers and build loyalty. PALCO dealer/distributor programs enable investment, build sales and expand your opportunities with an unmatched assortment of premium products and services that help your customers and you succeed. PALCO provides training materials, administrative assistance, technical support and everything needed to build a successful Dealer/distributorship. Own your own business, be your own boss.